Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn, one of the most prominent and influential figures in the history of Western art, was born in Leiden, Netherlands, on July 15, 1606. Today, he is celebrated for his unparalleled mastery of painting, drawing and engraving, but not He stood out not only for his excellent technical skill, but also for his deep understanding of human psychology and his ability to capture the essence of life in his works. With a career that spanned the Dutch Golden Age, Rembrandt became an icon of the Baroque era, redefining the boundaries of art and leaving a lasting artistic legacy that continues to inspire and fascinate generations to this day.
Throughout this article, we will explore Rembrandt's fascinating life, from his early education as an apprentice painter to his recognition as a master. We will investigate the innovative techniques he used in his works, as well as the recurring themes that drove him to create compositions rich in emotion and depth. Additionally, we will delve into the artistic revolutions that Rembrandt led, including his unique approach to light and shadow, his ability to portray humanity in all its diversity and complexity, and his ability to tell captivating stories through his works of art.
Through a thorough analysis of some of his most iconic works and the influences that shaped his career, this article seeks to shed light on Rembrandt's genius and his invaluable contribution to the world of art.
What is the story of Rembrandt's life and artistic career?
The life story and artistic career of Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn is a journey full of successes, challenges and innovations that established him as one of the most renowned artists in the history of art. Born in Leiden, Netherlands, on July 15, 1606, Rembrandt grew up in a middle-class family and showed an early interest in art. His father, a miller, supported his artistic inclination and enrolled him at Leiden University, where Rembrandt began studying art in 1620. However, he soon abandoned academic studies to pursue his artistic passion, becoming an apprentice to the painter Jacob van Swanenburgh.
After completing his training with Swanenburgh, Rembrandt joined the studio of renowned painter Pieter Lastman in Amsterdam, where he further expanded his artistic education. Lastman's influence is evident in some of Rembrandt's early works, which often explored historical and biblical themes.
The real milestone in Rembrandt's career came when he opened his own studio in Leiden around 1624. It was at this time that he began to develop his distinctive style, characterized by the dramatic use of light and shadow, known as chiaroscuro, which became a trademarks of their works. He also began to specialize in portraits and everyday scenes, demonstrating a remarkable ability to capture the emotional and psychological depth of his characters.
In 1631, Rembrandt moved to Amsterdam, the cultural and economic capital of the Netherlands at the time. His career flourished in the city, where he quickly gained fame and attracted an influential clientele. His studio became a place of learning for young artists and a center for artistic creation.
In addition to his mastery in painting, Rembrandt also excelled in engraving. His prints are notable for their technical complexity and emotional depth. He produced a series of innovative works, including self-portraits, biblical scenes and portraits of ordinary people.
However, Rembrandt's career also had its ups and downs. He faced financial difficulties due to an extravagant lifestyle and unsuccessful investments, which led to his bankruptcy in 1656. Even so, he continued to produce works of high quality.
The final period of his life was marked by personal tragedies, including the death of his wife and children. Despite the adversities, he continued to work and reinvent himself artistically, experimenting with new techniques and styles.
Rembrandt passed away on October 4, 1669, leaving behind a lasting artistic legacy and an immeasurable influence on future generations of artists. His ability to explore humanity in depth, his technical mastery and his commitment to challenging established artistic conventions have secured his place as one of the undisputed masters of Western art. His works continue to be studied, admired and celebrated as vivid witnesses to the transformative power of artistic expression.

What are the characteristics of Rembrandt's works?
Rembrandt's works are known for their distinctive characteristics that set him apart as one of the most iconic and influential artists in the history of art. His creations transcend conventional boundaries, exploring human and visual themes in innovative and profound ways. Some of the main characteristics of his works include:
Domain of Light and Shadow: Rembrandt is widely recognized for his exceptional mastery of chiaroscuro, a technique that involves the dramatic use of contrasts between light and shadow. He used light to highlight specific areas of his compositions, creating a sensation of remarkable depth and volume. This approach contributed to the creation of intense emotional atmospheres and helped to focus the viewer's attention on the key elements of the scene.
Texture and Brushstrokes: Rembrandt's loose, expressive brushwork added texture and depth to his works. He was not concerned with perfect smoothness, allowing visible brushstrokes to give life and dynamism to his paintings.
Portraits with Psychological Depth: Rembrandt had a unique ability to capture the personality and emotion of his subjects. His portraits often show remarkable psychological depth, revealing the inner complexities of the people he portrayed. He went beyond the physical surface and captured the essence and humanity of his models.
Expressive Self-Portraits: Rembrandt is also famous for his series of self-portraits, in which he explored his own aging, emotions and states of mind. These works reveal an intimate self-awareness and a frank exploration of physical and psychological transformations over time.
Thematic Variety: His work covers a wide range of themes, including religious, mythological, historical and everyday scenes. Regardless of the subject matter, his paintings often seem to capture fleeting moments and powerful narratives, urging the viewer to become emotionally involved with the scene.
Expressive Painting Technique: Rembrandt's brushwork technique is characterized by loose, expressive brushstrokes, which add texture and depth to his paintings. This approach contributes to the feeling of movement and life in the works.
Realistic Details and Textures: In his works, Rembrandt often included meticulously realistic details and textures, making his paintings visually rich and engaging. This is particularly visible in his still life scenes and luxurious clothing.
Narrative and Atmosphere: Many of Rembrandt's paintings seem to freeze moments in stories, inviting the viewer to imagine what happened before or after the scene depicted. The immersive atmosphere and careful use of light and shadow contribute to the construction of these suggestive narratives.

What are Rembrandt's most famous works?
Rembrandt produced a vast amount of works throughout his career, many of which have become icons of Western art. Some of Rembrandt's most famous and widely recognized works include:
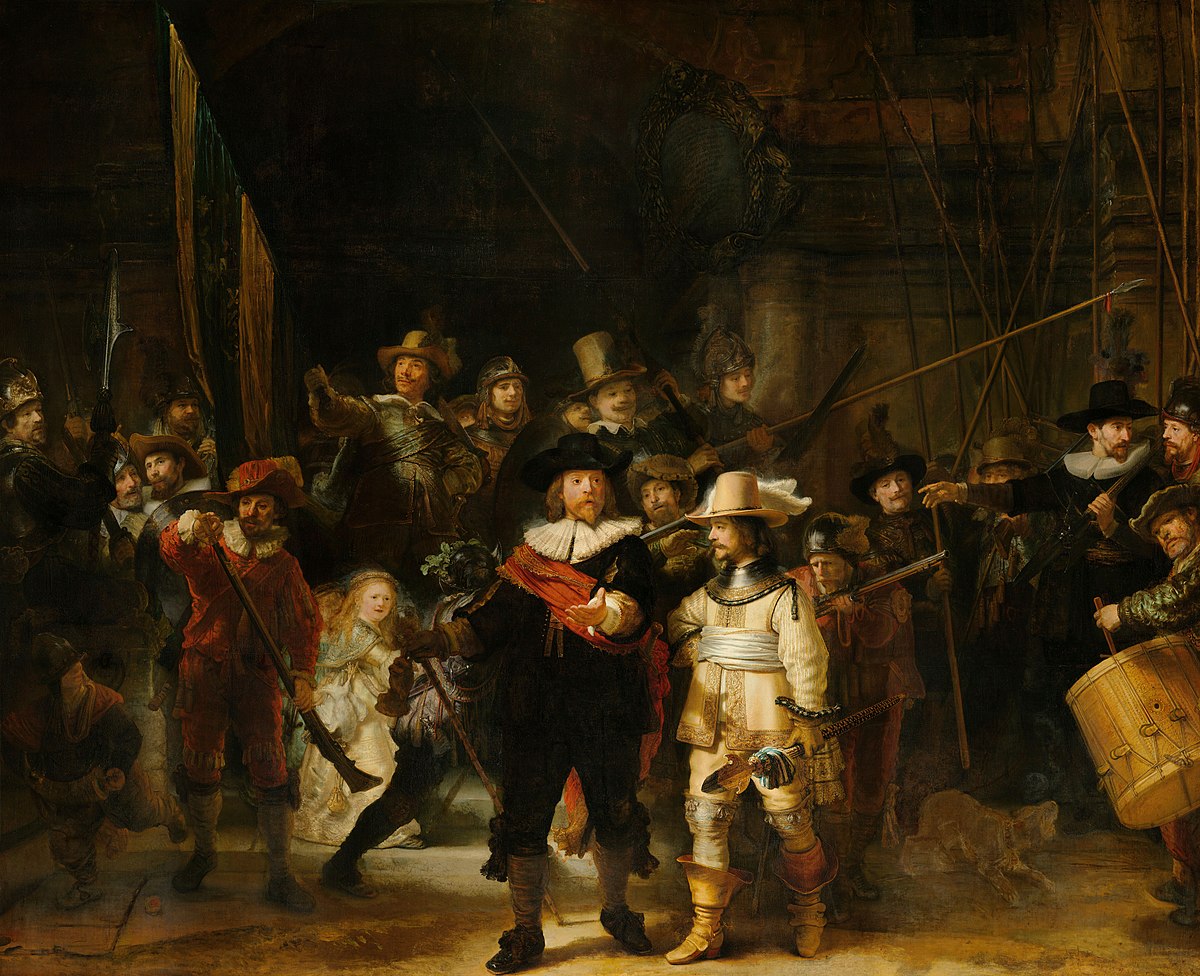
"The Night Watch" (1642): Also known as "The Militia of Captains Frans Banning Cocq and Willem van Ruytenburch", this painting is one of Rembrandt's most famous and iconic. It portrays a Dutch militia company in a moment of action and movement, with masterful use of light and shadow to emphasize the main characters.
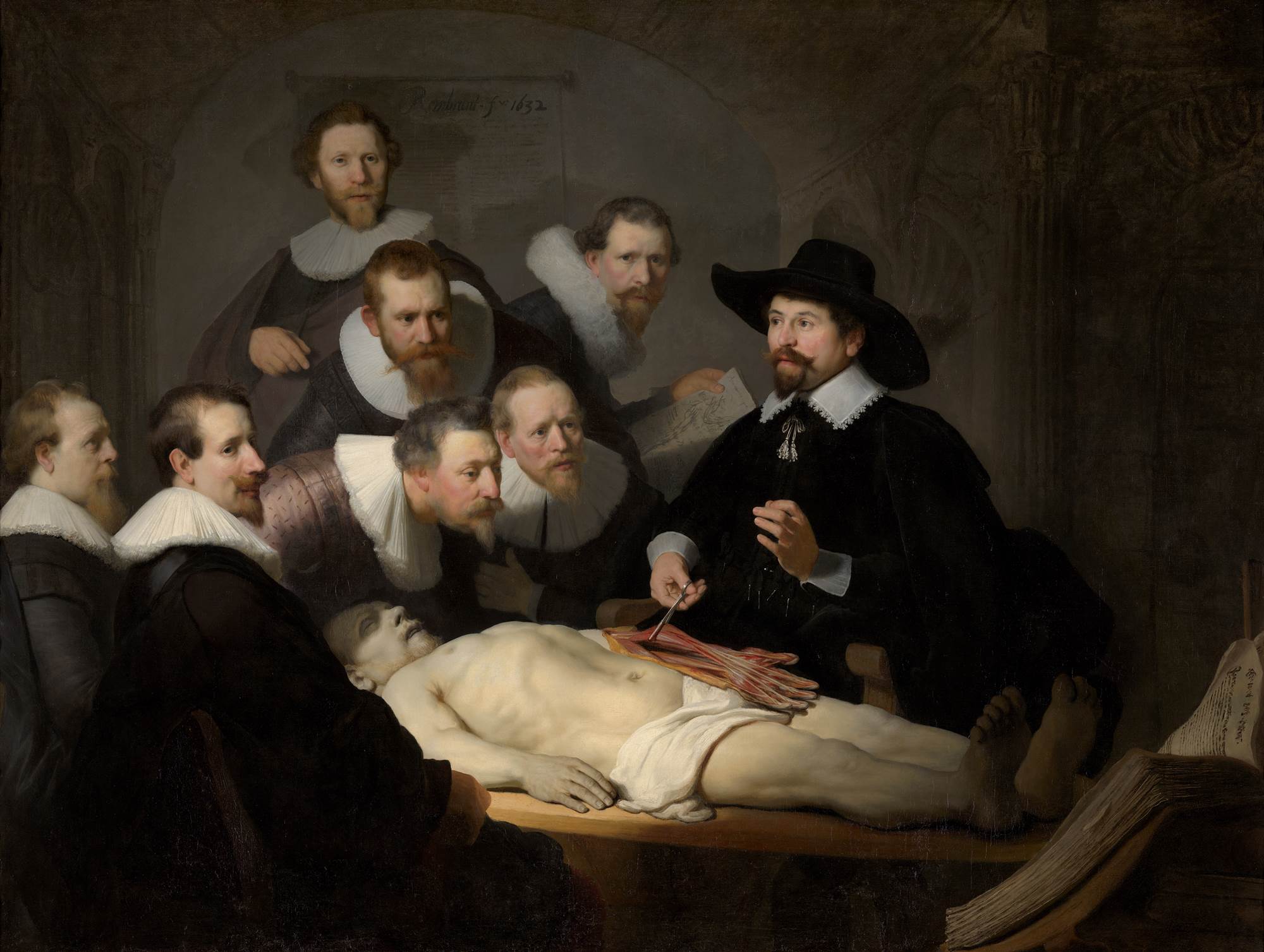
"The Anatomy Lesson of Dr. Nicolaes Tulp" (1632): In this work, Rembrandt portrays an anatomy class led by the doctor Nicolaes Tulp. The painting is notable for its anatomical precision and the way the artist captures the atmosphere of the class and the expressions of those present.
"The Prodigal Son" (1669): This emotional and deeply moving work portrays the moment when the prodigal son returns to his father's house after having squandered his inheritance. The scene is full of emotion and symbolism, and Rembrandt uses light to emphasize the moment of reconciliation.
"Portrait of Jan Six" (1654): In this portrait, Rembrandt masterfully captures the personality and presence of young Jan Six, a friend of the artist. The painting is notable for its approach to individual portraiture, highlighting the psychological depth of the subject.
"The Music Lesson" (c. 1626): In this genre scene, Rembrandt depicts an intimate moment of a music lesson between a young woman and a gentleman. The painting demonstrates the artist's ability to create realistic atmospheres and capture the emotions of the figures represented.
Self-portrait Series: Rembrandt produced a series of self-portraits throughout his career, showing himself at different ages, moods and situations. Each of these self-portraits offers a unique window into the artist's mind and his evolution over time.

What were Rembrandt's influences?
Rembrandt's art was influenced by a variety of factors, including other artists, contemporary techniques, historical events, and cultural contexts. Some of the key influences that shaped Rembrandt's style and approach include:
Caravaggio and Chiaroscuro: The work of Italian painter Caravaggio had a significant influence on Rembrandt, especially in relation to his dramatic use of light and shadow, known as chiaroscuro. Rembrandt studied Caravaggio's works and adapted this technique to his own style, creating dramatic lighting effects in his paintings.
Engraving Techniques: Rembrandt was also a master engraver, and his skills in this area were influenced by engravers such as Lucas van Leyden and Albrecht Dürer. He experimented with a variety of printmaking techniques, exploring textures and shadows in innovative ways.
Dutch Art Scene: Rembrandt was part of the thriving art scene in the Netherlands during the Dutch Golden Age. He was aware of the artistic trends and contemporary influences of his time, which helped him develop a distinctive style within that context.
Still Life and Genre Scenes: The tradition of Dutch still lifes and genre scenes also had an impact on Rembrandt. He often included these elements in his works, demonstrating detailed attention to everyday objects and texture.
Literature and Theater: Rembrandt's visual storytelling and dramatic expression may have been influenced by the literature and theater of the time. His ability to create emotional and captivating stories in his paintings may have been inspired by literary narratives and the theatrical performances that were popular in his time.
Life and Personal Experience: Rembrandt's personal experiences and life events also shaped his art. His own emotions, joys, sadness and challenges can be seen in many of his works, especially in his self-portraits, which reflect his personal evolution over time.
Innovation and Personal Experimentation: One of Rembrandt's most striking characteristics was his willingness to experiment and innovate. He was willing to challenge the artistic conventions of the time, adapting and developing new techniques and approaches to create unique and powerful works.
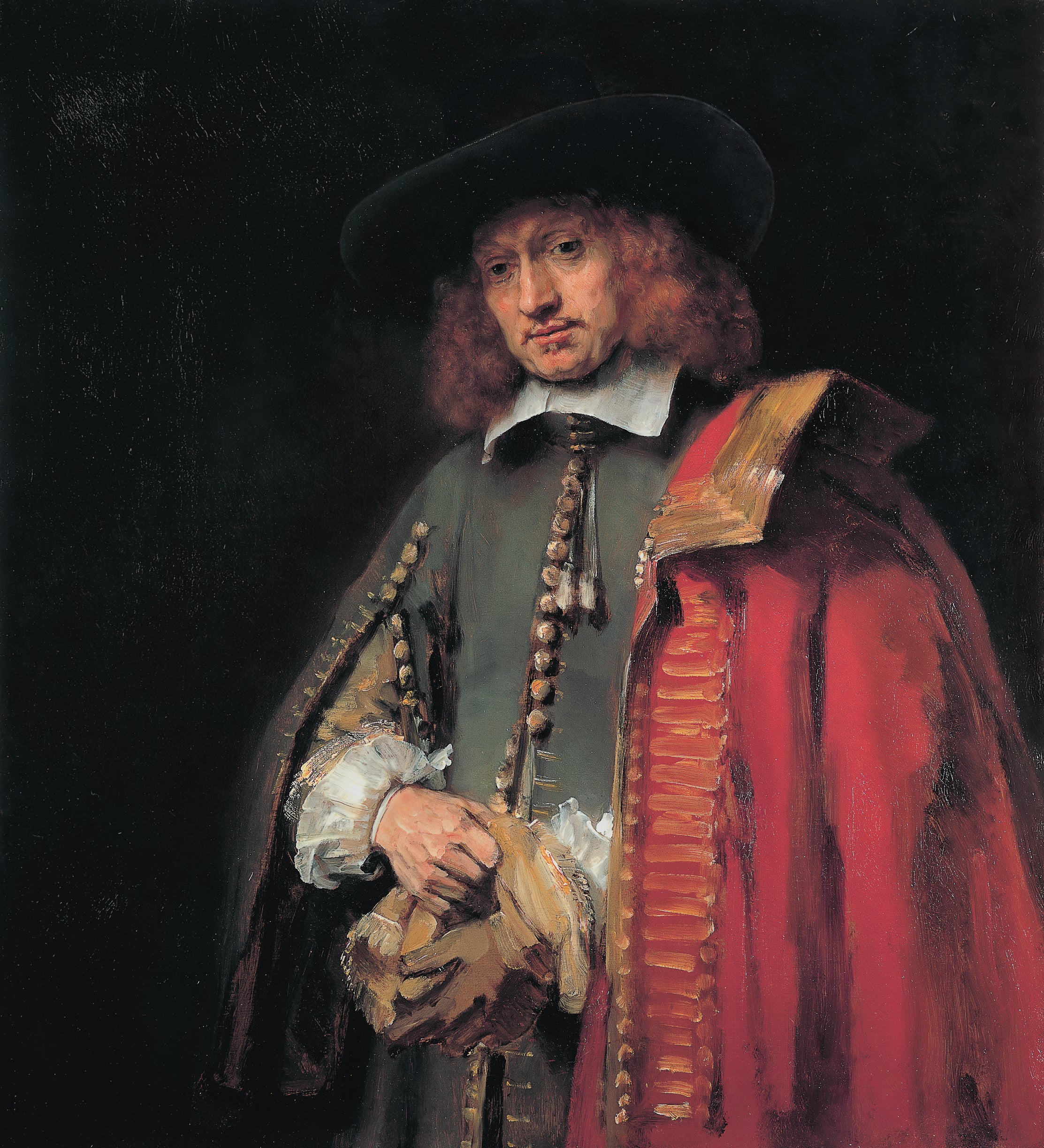

Why is Rembrandt so special?
Rembrandt is considered special and one of the most revered artists in the history of art for several reasons, which reflect his lasting influence and unique contribution to the art world:
Technical Domain: Rembrandt's technical skill is remarkable and is often considered impeccable. His mastery of light and shadow, detailed texture, expressive brushwork and anatomical precision demonstrate his mastery in the various artistic disciplines in which he worked.
Artistic Innovation: Rembrandt was an innovator who challenged the established conventions of his time. He explored new painting and engraving techniques, creating impressive light and shadow effects that brought his works to life. His unique approach to representing human psychology and visual storytelling also contributed to his uniqueness.
Emotional Depth: His paintings are full of emotion and psychological depth. Rembrandt had the remarkable ability to capture the essence of human emotions, allowing his characters to connect directly with viewers.
Psychological Portraits: Rembrandt's portraits go beyond the physical representation of his models. He managed to reveal the personality and soul of the people portrayed, creating portraits that are more than simple external representations.
Thematic Variety: Its wide range of themes, which include religious, mythological, historical and everyday scenes, reflects its versatility and ability to engage with diverse aspects of human life and society.
Self-portraits as Self-Exploration: Rembrandt produced a series of self-portraits throughout his life, which was unusual at the time. These self-portraits served as a form of self-exploration, allowing him to examine his own identity and aging.
Lasting Legacy: Rembrandt's influence extends beyond his own era. His innovative style and artistic approaches continue to inspire generations of artists, from his time to the present day. His ability to touch humanity and convey emotions ensures that his works remain relevant and moving over time.
Contribution to Baroque Art: Rembrandt played a crucial role in the evolution of Baroque art, leaving an indelible mark on this artistic period. His unique approach to light and shadow, his emphasis on human emotion, and his exploration of realism and spirituality contributed to the enrichment and redefinition of the Baroque movement.
Overall, the combination of technique, innovation, emotional depth and artistic legacy distinguishes Rembrandt as one of the most special and influential artists in the history of art. His ability to create works that resonate with the human experience transcends borders and continues to captivate people around the world, making him truly exceptional.

